
Matter consists of small particles called molecules which again consist of atoms. The sub-atomic particle discovered by Rutherford through his Alpha (α) Particle Scattering Experiment was the Nucleus. Question 3: Which sub-atomic particle was discovered by Rutherford through his Alpha (α) Particle Scattering Experiment? However, the experiment produced entirely unanticipated results. Rutherford didn’t expect to witness significant deflections as the α-particles were considerably heavier than the protons. The hypothesis was that α-particles would be deflected by the sub-atomic particles in the gold atoms. Rapidly-moving α-particles possess a great deal of energy, as they have a mass of about 4 amu.

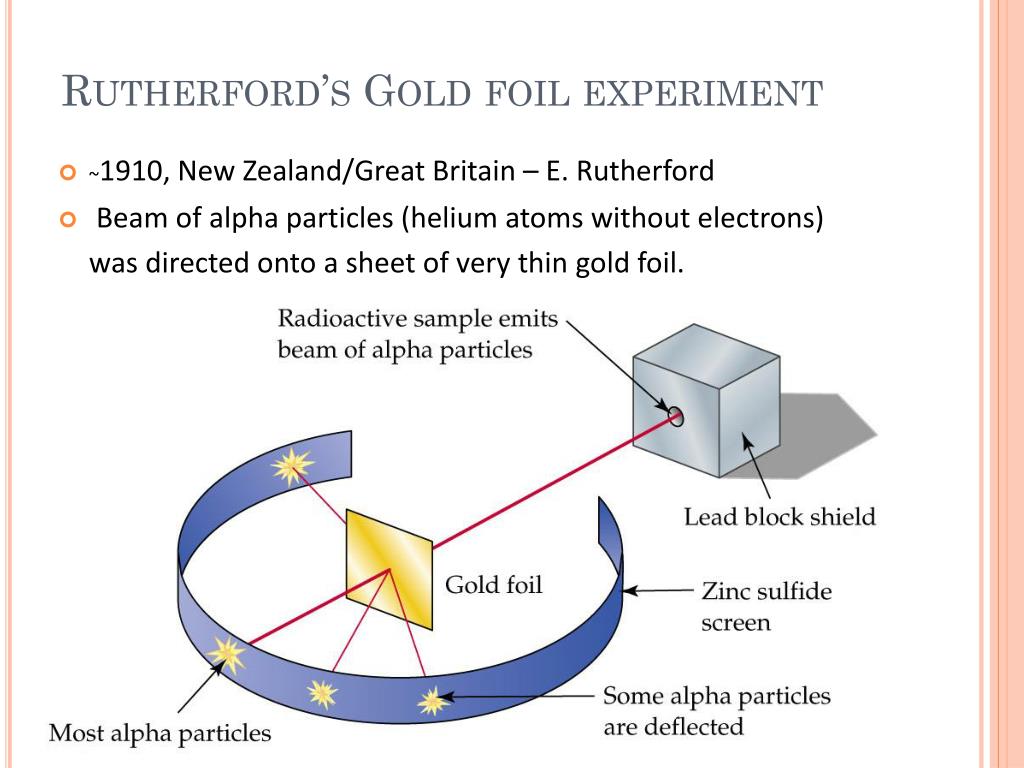
Doubly-charged helium ions are known as α-particles. The thickness of the gold foil was about 1000 atoms. The gold foil was selected so as to obtain an extremely thin layer. Rapidly-moving α-particles were directed to bombard a thin sheet of gold. To determine how electrons are arranged in an atom, the Alpha (α) Particle Scattering Experiment was organized by Rutherford. Question 2: Briefly explain Rutherford’s scattering experiment. It could not explain Rutherford’s scattering experiment. The nucleus of an atom is not mentioned in the hypothesis. It also fails to explain the stability of an atom. Thomson’s atomic model does not explain how the positive charge on the electrons inside the atom is maintained.
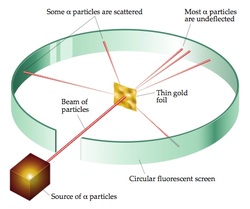
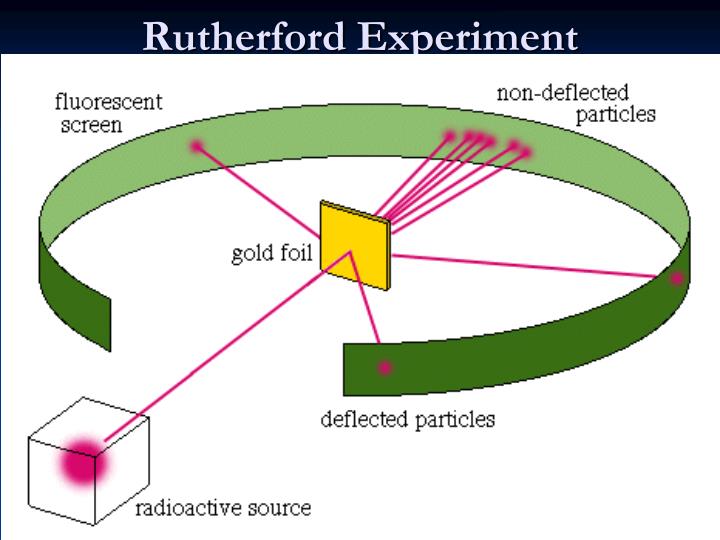
Positively charged particles make up an atom.Here are the major postulates of Rutherford’s atomic model based on observations and conclusions: As a result, he came to the conclusion that the positively charged particles only occupied a small portion of an atom’s overall volume. In addition, relatively few particles had 180o deflected. Very few alpha particles had deflected back or at large angles.They experienced extremely slight angles of deflection. When bombarded, the gold foil only deflected a small number of alpha particles. The positive charge in an atom is concentrated in a relatively small volume and is not dispersed evenly.As a result, an atom’s main portion must be empty. A large percentage of alpha particles traveled through the gold film without being deflected, indicating that the majority of space in an atom is empty.Rutherford observed the following from his α-particle scattering experiment: ISRO CS Syllabus for Scientist/Engineer Exam.ISRO CS Original Papers and Official Keys.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
